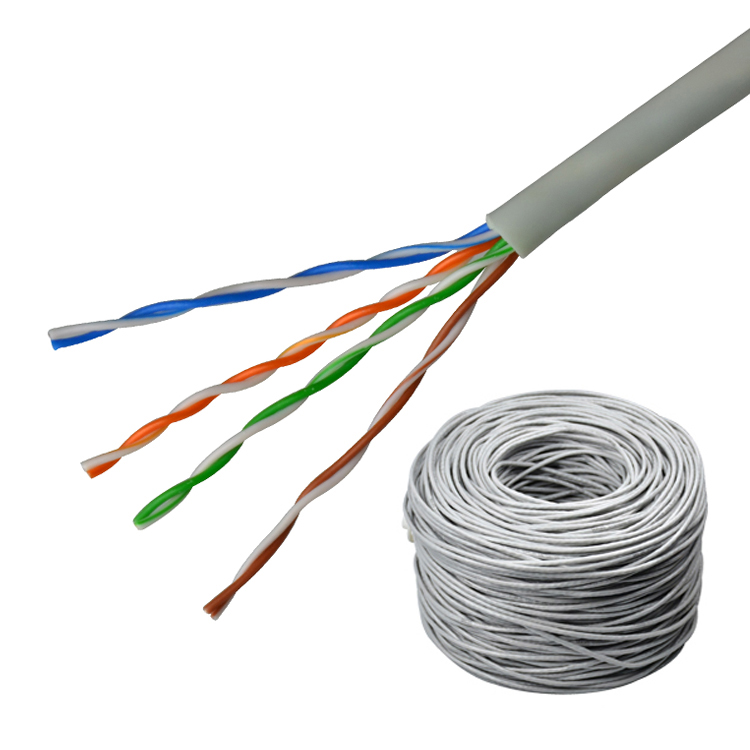
Hello, welcome to Jiexi kunlian cable co.,Ltd , in this article, we will discuss the network cables transmission speed.
There are also university questions about small network cables, which cannot be ignored. Friends who know more about the network know that network cables have transmission distances. For example, in the integrated wiring specification, it is also clearly required that the horizontal wiring cannot exceed 90 meters and the total link length cannot exceed 100. Meters, that is, one hundred meters is a limit for wired Ethernet, this limit is the link length from the network card to the hub device.
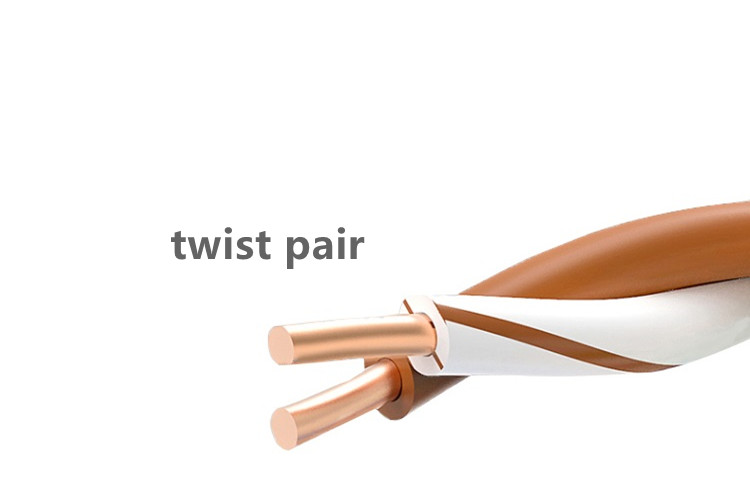
Twisted pair has an “insurmountable” transmission distance of “100 meters”, whether it is a Category 3 twisted pair with a transmission rate of 10 meters, or a Category 5 twisted pair with a transmission rate of 100 meters, or even a transmission rate of one kilometer. The maximum effective transmission distance of the six types of twisted-pair cables is 100 meters. The physical factors of the twisted-pair cable largely determine the quality of the network cable. Inferior network cables often use unqualified twisted-pair core wire winding methods, which are inexpensive The metal core wire achieves the purpose of cutting corners, and this irresponsible behavior directly aggravates the interference of the network signal in the network cable, so that the effective transmission distance of the network cable is far less than 100 meters, and it will also affect the stability of the network transmission. And the service life of the network cable.
Transmission distance of various network cables
Category 5 and Category 6 are 100 meters, coaxial cable thin cable 185 meters, thick cable 500 meters Optical fiber 1 Transmission rate 1Gb/s, 850nm (fiber diameter)
- Ordinary 50μm multimode fiber transmission distance is 550m b, ordinary 62.5μm multimode fiber transmission distance is 275m c, new 50μm multimode fiber transmission distance is 1100m
2 Transmission rate 10Gb/s, 850nm:
- Ordinary 50μm multimode fiber transmission distance is 250m b, ordinary 62.5μm multimode fiber transmission distance is 100m c, new type 50μm multimode fiber transmission distance is 550m. …
- Transmission rate 2.5Gb/s, 1550nm
a, g.652 single-mode fiber transmission distance is 100km b, g.655 single-mode fiber transmission distance is 390km
- Transmission rate 10Gb/s, 1550nm
a, g.652 single-mode fiber transmission distance of 60km b, g.655 single-mode fiber transmission distance of 240km
- The transmission rate is 40Gb/s, 1550nm a, g.652 single-mode fiber transmission distance is 4km b, g.655 single-mode fiber transmission distance is 16km
- a, g.652 single-mode fiber transmission distance of 60km b, g.655 single-mode fiber transmission distance of 240km
- The transmission rate is 40Gb/s, 1550nm a, g.652 single-mode fiber transmission distance is 4km b, g.655 single-mode fiber transmission distance is 16km
Maximum cable distance during actual construction
It can be seen from the above that when using PoE power supply, why the maximum length of the network cable should not exceed 100 meters. However, in actual construction, in order to ensure the quality of the project, it is generally 80-90 meters. Please note that the transmission distance here refers to the maximum rate, such as 100M. If the rate is reduced to 10M, the transmission distance can usually be extended to 150-200 meters, so the PoE power transmission distance is not determined by PoE technology. It is determined by the type and quality of the network cable. To
Although in actual construction, a better-quality network cable can break the 100-meter distance limit and the equipment can also work normally, this approach is not recommended. Because some potential problems will not appear immediately, but slowly appear over time, which will cause follow-up maintenance problems. The simplest case is, for example, the bandwidth upgrade, so that the equipment that can work normally at a distance of more than 100 meters will not work normally after the network speed is greatly increased.
How did you get the maximum distance of one hundred meters?
What caused the 100-meter transmission distance limit for twisted-pair cables? It is necessary to delve into the deep physical principles of twisted pair. The transmission of the network is actually the transmission of the network signal on the twisted pair. As an electronic signal, when it is transmitted in the twisted pair, it must be affected by resistance and capacitance, which leads to the attenuation and distortion of the network signal. When the signal attenuation or distortion reaches a certain level, it will affect the effective and stable transmission of the signal. Therefore, the twisted pair cable has a transmission distance limit, so how do you calculate the upper limit of 100 meters?
Category 5 UTP and Category 5 UTP are mainly used for computer network services. According to the 100Base-TX regulations of Fast Ethernet, the communication rate is 100mbps. The time it takes for 100mbps Ethernet to transmit 1 bit of data can be calculated as follows: 1 bit time =1/100mbps=10ns Ethernet uses CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection), that is, carrier sense multiple access technology with collision detection to share communication channels. After switching is introduced, this technology is still inseparable . There are devices at both ends of a link. The two devices may send data at the same time, causing conflicts. At this time, the conflict domain is 2. Data packets will be lost due to conflicts. In order to avoid packet loss caused by conflicts, Ethernet uses conflict detection and back-off retransmission technology. In order to back off and retransmit, it is necessary to ensure that one end can detect the conflict before transmitting a data packet.
The minimum frame length of Ethernet is 64 bytes, which is 512 bits. Calculated at a rate of 100mbps, it takes 512 bits*10ns=5120ns to transmit 512 bits. Data information is transmitted in the network, and there will be delays when passing through different components, five types The delay of UTP is 5.56ns/m. When designing Ethernet, a relay rule is required. This rule is also called the golden rule or 5-4-3-2-1 rule. This rule is not only applicable to 10mbps ether Net, it also applies to Fast Ethernet. This rule requires that the ring collision delay should not exceed 512 bits. For a transmission rate of 100mbps, it is 5120ns. In the loop, the network components include cables, relay units, MAU, and DTE. Add their delays and multiply them by two to get the loop delay. At the same time, the loop conflict diameter can also be calculated. According to this theory, Calculate the longest distance that the signal can be transmitted to ensure that a minimum frame is sent. This is why the link span is limited to 100 meters.
When it exceeds 100 meters, because the conflict cannot be detected in time, the transmission of the information packet damaged by the conflict is completed and received by the receiver. The information packet is forced to be discarded because it fails the verification. At this time, the mechanism of retransmission is not Is activated, so it will cause packet loss. When the transmission rate is lower than 100 mbps, in actual applications, the 100-meter limit can be appropriately relaxed. It must be stated that although this is actually effective, it does not meet the standard. It must be explained during the certification test, otherwise it will There may be some problems, such as product warranty.
The influence of cable type and quality on transmission distance
We are talking about three types of wires, five types of wires, seven types of wires…the difference between them is that the diameter of the copper wire is getting thicker, the torque is getting smaller and smaller, the twisting of the two cables is getting tighter and the wire pair There are more and more spacers (cross frame, aluminum foil, Mylar, drain wire, copper wire woven mesh), and the frequency ranges from 16MHz to 100MHz, 250MHz, 500MHz, 600MHz and so on. To
When the frequency increases, the crosstalk phenomenon becomes more and more serious. This requires increasing the diameter of the copper wire, increasing the torque of the cable, increasing the cross frame to separate the cables, increasing the thickness of the outer sheath or increasing the shielding layer, etc. Various production processes are used to solve the increasingly difficult crosstalk problem. It has to be said that crosstalk makes the cable structure more and more complicated. Category 5 cable is the most common standard network cable on the market, but the quality of different manufacturers is very different. Especially in the domestic price-oriented environment, many manufacturers use
copper-clad iron to reduce costs. The replacement of copper-clad steel leads to a decrease in the transmission distance of the network cable, and even network instability, packet loss, etc., and equipment manufacturers often have a scapegoat, which is really wrong. Therefore, if PoE is to achieve the best effect, it must be of good quality. The network cable should not affect the overall quality of the project due to small losses.
(1) CAT-5e cable: Compared with CAT-5 twisted-pair cable, CAT-5e twisted-pair cable has smaller attenuation and crosstalk, which can provide a more solid network foundation and meet most application requirements (especially supporting Gigabit Ethernet). Wiring of the network 1000Base-T), which brings convenience to the installation and testing of the network, and has become a better solution in current network applications. The transmission characteristics of CAT-5 cables are the same as those of ordinary CAT-5 cables, but CAT-5 cabling standards stipulate that all 4 pairs of CAT-5 cables can realize full-duplex communication.
(2) Category 6 cable: The transmission frequency of this type of cable is 1MHz~250MHz, and the comprehensive attenuation crosstalk ratio (PS-ACR) of Category 6 wiring system should have a larger margin at 200MHz, which provides 2 times that of Category 5 Bandwidth. The transmission performance of Category 6 cabling is much higher than the Category 5 Super Standard, and is most suitable for applications with a transmission rate higher than 1Gbps. To
(3) An important difference between Category 6 and Category 5 is: improved crosstalk and return loss performance. For a new generation of full-duplex high-speed network applications, excellent return loss performance is extremely important. Importantly, the basic link model is cancelled in the six types of standards, and the wiring standard adopts a star topology. To
(4) The required wiring distance is: the length of the permanent link cannot exceed 90 meters, and the channel length cannot exceed 100 meters. There is no strict difference in the transmission distance between Cat 6 line and Cat 5 line, that is, the maximum transmission distance of a single segment is both It is 100 meters. Of course, the transmission distance of Category 6 lines can be appropriately increased. The so-called 100 meters means that the 1000M bandwidth and other related technical indicators cannot be met after exceeding, which will cause problems such as speed drops.
The higher the transmission rate of the network cable, the higher the frequency and the stronger the interference caused, which requires higher shielding means. In low-end twisted-pair products, the winding distance is a main reference for the pros and cons, but in higher-end twisted-pair products, not only the winding distance of the core wire should be considered, but also the crosstalk shielding means However, when it comes to the signal crosstalk shielding of the network cable, we can also divide the network cable into shielded twisted pair and unshielded twisted pair from this perspective. The unshielded twisted pair is divided into 4 pairs and twisted together by 8 wires of different colors. The function of twisting in pairs is to minimize the influence of electromagnetic radiation and external electromagnetic interference. According to the different shielding methods, shielded twisted pair cables are divided into two categories, namely STP (Shielded Twisted-Pair) and FTP (Foil Twisted-Pair). STP refers to a shielded twisted pair with its own shielding layer for each line, while FTP is a shielded twisted pair with an overall shield. The shielded twisted pair has a higher transmission rate, which can reach 155Mbps within 100 meters, which is higher than the corresponding unshielded twisted pair. At present, most of our common types of network cables are unshielded twisted-pair cables. This is also the wiring transmission medium used in most local area networks today, using unshielded twisted pair networking, the network cable is composed of a certain distance long twisted pair and RJ45 heads.

Some people may ask, since shielded twisted pair cable is faster than unshielded twisted pair in anti-interference and transmission, why don’t people use shielded category five twisted pair? This is because the shielded twisted pair requires that the entire system be shielded devices, including cables, sockets, crystal plugs, and distribution frames. At the same time, the building needs a good grounding system. The harsh environmental conditions of the shielded twisted pair are destined The “fragility” of this technology. Generally speaking, in actual construction, it is difficult to ground perfectly, so that the shielding layer itself becomes the largest source of interference, resulting in performance that may even be inferior to unshielded twisted pair. Therefore, unless there are special needs, usually only unshielded twisted pairs are used in the integrated wiring system. To
The unshielded twisted pair uses physical principles to reduce signal crosstalk, while also bringing cost reductions and the robustness of network cabling. Although shielded twisted pair is superior to unshielded twisted pair in principle, its technical fragility and high capital investment have become a weakness. When choosing between the two directly, you need to be careful. If you really need higher network quality and longer transmission distance, users can use the method of installing a repeater between two twisted pairs to achieve better wiring cost performance. (It is recommended to install 4 repeaters at most, and more repeaters will also affect network transmission).


